链表与 LRU 缓存淘汰算法
数组与链表在内存分布上的不同之处,数组需要连续的内存空间,链表则不需要。
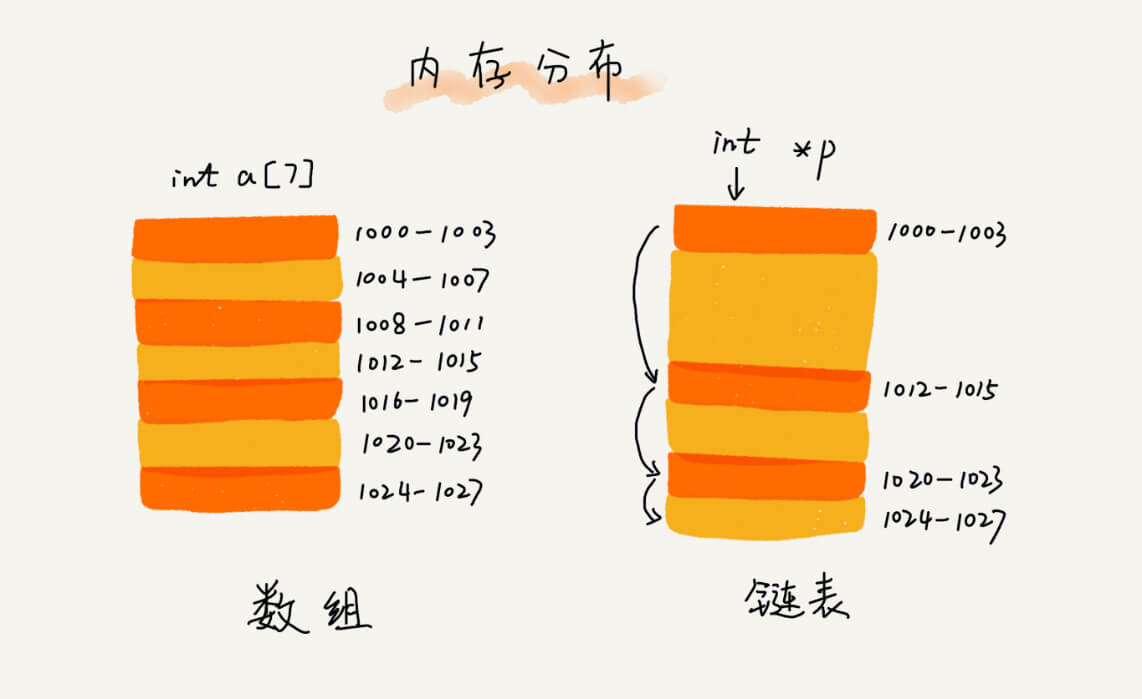
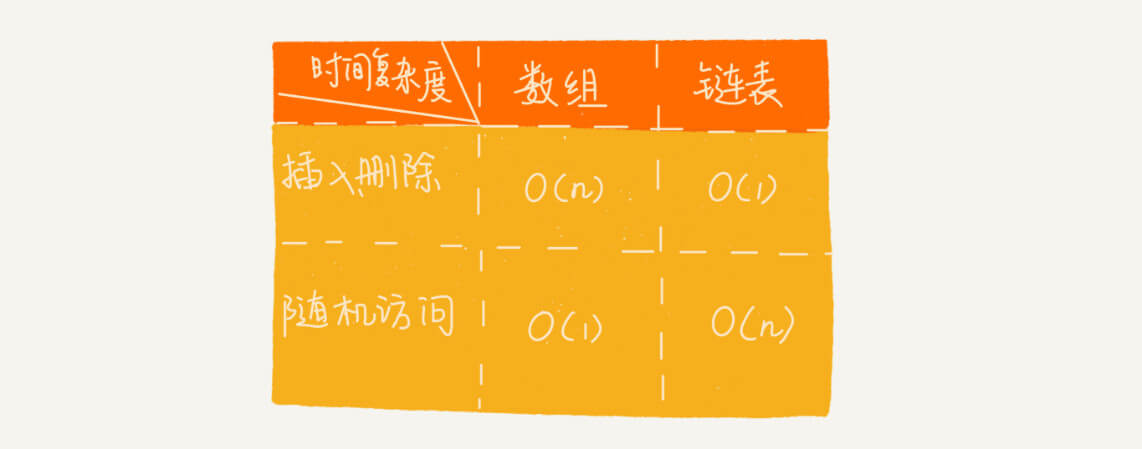
数组与链表的性能比较:
LeetCode 上也有对应的题目,146. LRU Cache 。
LRU 算法在 iOS 上的应用
YYCache 算是一例,通过双向链表结合 NSDictionary 使得增、删、改、查、清空的时间复杂度都是 O(1) 。具体实现代码在 YYMemoryCache.m 这个类里面。
练习题:判断链表是否为回文链表
Palindrome Linked List - LeetCode
如何写出正确的链表代码
重点留意边界情况。
栈
经典应用场景:函数调用栈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
int main() {
int a = 1;
int ret = 0;
int res = 0;
ret = add(3, 5);
res = a + ret;
printf("%d", res);
reuturn 0;
}
int add(int x, int y) {
int sum = 0;
sum = x + y;
return sum;
}
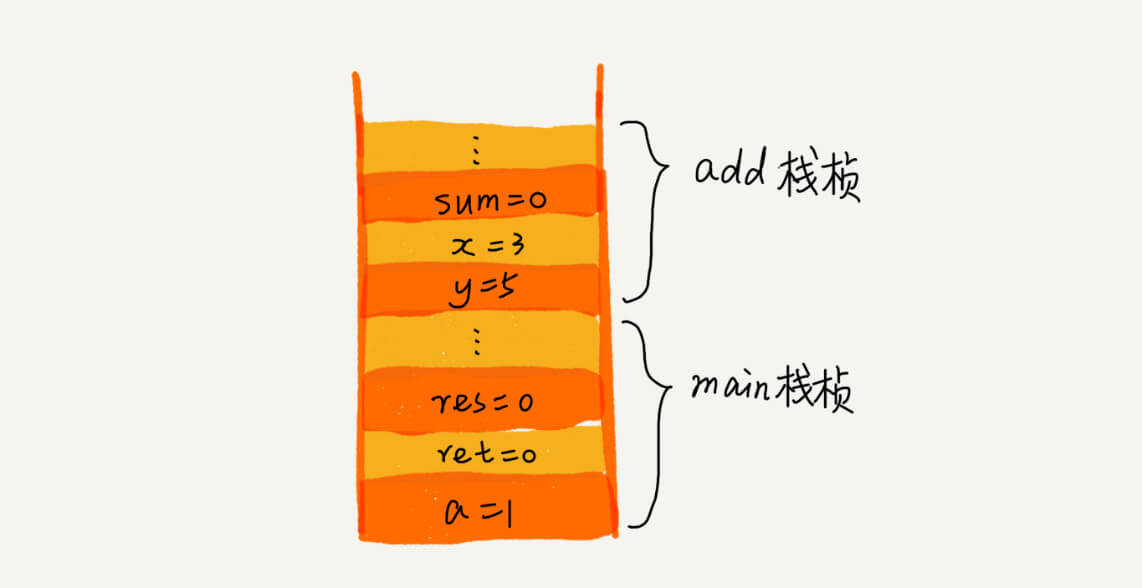
还有表达式求值,括号匹配,浏览器的前进后退等。
队列
使用循环队列来避免数据搬移。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public class CircularQueue {
// 数组:items,数组大小:n
private String[] items;
private int n = 0;
// head表示队头下标,tail表示队尾下标
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
// 申请一个大小为capacity的数组
public CircularQueue(int capacity) {
items = new String[capacity];
n = capacity;
}
// 入队
public boolean enqueue(String item) {
// 队列满了
if ((tail + 1) % n == head) return false;
items[tail] = item;
tail = (tail + 1) % n;
return true;
}
// 出队
public String dequeue() {
// 如果head == tail 表示队列为空
if (head == tail) return null;
String ret = items[head];
head = (head + 1) % n;
return ret;
}
}
阻塞队列和并发队列
阻塞队列其实就是在队列基础上增加了阻塞操作。简单来说,就是在队列为空的时候,从队头取数据会被阻塞。因为此时还没有数据可取,直到队列中有了数据才能返回;如果队列已经满了,那么插入数据的操作就会被阻塞,直到队列中有空闲位置后再插入数据,然后再返回。
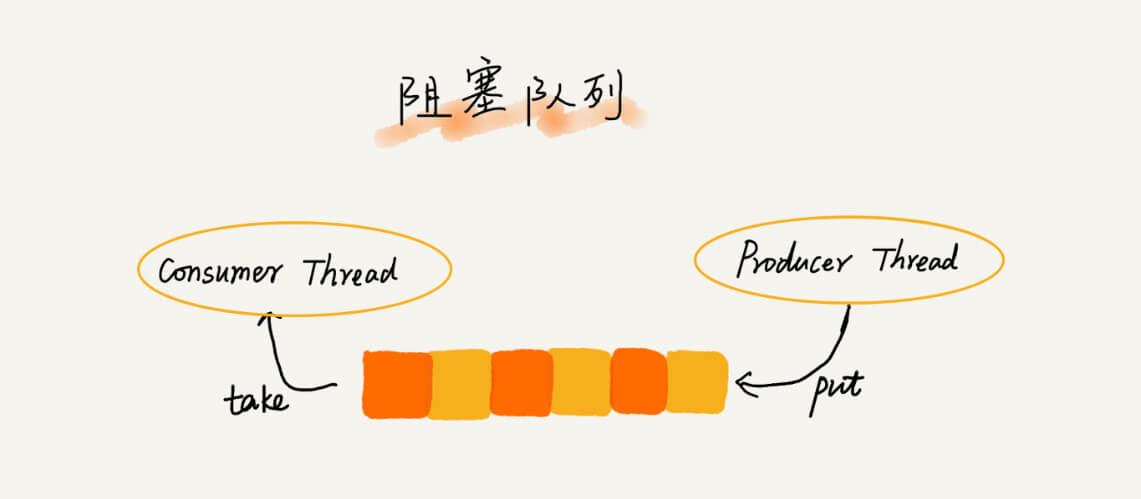
对于大部分资源有限的场景,当没有空闲资源时,基本上都可以通过“队列”这种数据结构来实现请求排队。
Comments powered by Disqus.